
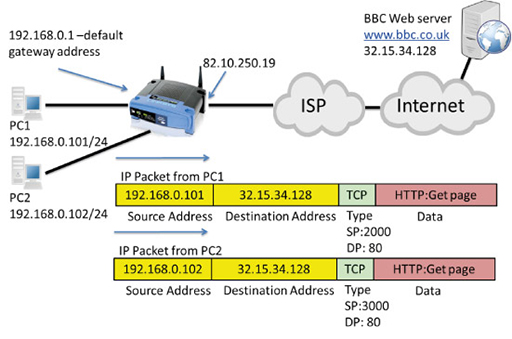
Unable to detect any alternate path that may be available. Results in a catastrophic event, isolating all end-hosts that are However, thisĬreates a single point of failure. Protocols are deployed, which typically provide configurationįor an end-host IP address and default gateway. Operation is likely to persist as dynamic host configuration Is supported by virtually every IP implementation. Minimizes configuration and processing overhead on the end-host and The use of a statically configured default route is quite popular it The detection of a lost (i.e., dead) neighbor, that may introduce This can result in a significant delay in Leading to large timer values to reduce protocol overhead in the face Protocols may require active participation by all hosts on a network, Overhead, processing overhead, security issues, or lack of a protocol Infeasible for a number of reasons, including administrative Running a dynamic routing protocol on every end-host may be

Routing Information Protocol or OSPF version 2, runningĪn ICMP router discovery client or using a statically Include running (or snooping) a dynamic routing protocol such as Its first hop router towards a particular IP destination. There are a number of methods that an end-host can use to determine Operation over FDDI, Token Ring, and ATM LANE. Minimization of Unnecessary Service Disruptions. Path without requiring configuration of dynamic routing or routerġ. TheĪdvantage gained from using VRRP is a higher availability default The LAN to be used as the default first hop router by end-hosts. This allows any of the virtual router IP addresses on In the forwarding responsibility should the Master become The election process provides dynamic fail over The VRRP router controlling the IP address(es) associated withĪ virtual router is called the Master, and forwards packets sent to Responsibility for a virtual router to one of the VRRP routers on a VRRP specifies an election protocol that dynamically assigns This memo defines the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP). Distribution of this memo is unlimited.Ĭopyright (C) The Internet Society (2004).
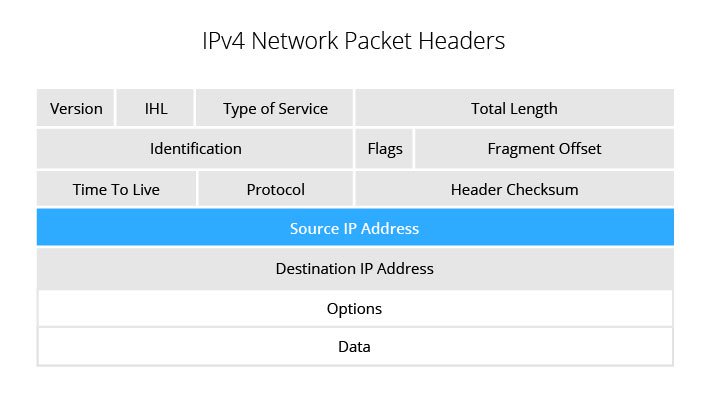
Official Protocol Standards" (STD 1) for the standardization stateĪnd status of this protocol. Please refer to the current edition of the "Internet Internet community, and requests discussion and suggestions for This document specifies an Internet standards track protocol for the Tcpdump is a complex and powerful tool to view packets.Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) OS X / Linux: sudo tcpdump -nnSX port 80 (visit after running this command).
OS X / Linux : sudo tcpdump -nnSX port 443
#DETERMINE IP AND MAC HEADER INFORMATION FOR A DATA PACKET HOW TO#
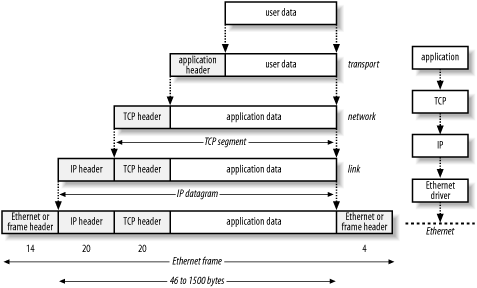
It will take you many hours to learn how to use wireshark. The de-facto tool for this stuff is wireshark. Diagnosing network problems via packet analysis is not within the scope of IB Computer Science, but you should be able to view a network packet. You should be aware how to capture and view packets. Looking for a basic introduction to packets ?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
